2025년 05월 Comparative Analysis of Mitochondrial and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation for Angiogenesis and Muscle Regeneration
첨부파일
-
 2025-06 Comparative analysis of mitochondrial and mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for angiogenesis and muscle regeneration.pdf
(3.7M)
7회 다운로드
DATE : 2025-06-13 14:32:40
2025-06 Comparative analysis of mitochondrial and mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for angiogenesis and muscle regeneration.pdf
(3.7M)
7회 다운로드
DATE : 2025-06-13 14:32:40
관련링크
본문
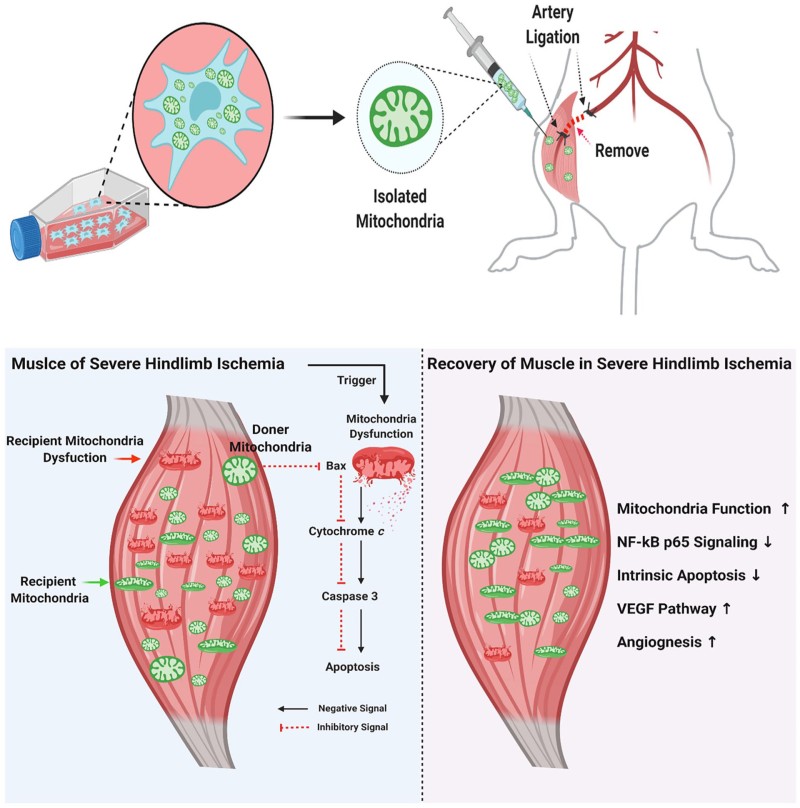
Mitochondrial transplantation has emerged as a promising strategy for treating ischemic diseases by restoring mitochondrial function in damaged tissues. This study investigated the therapeutic potential of mitochondria isolated from placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (PD-MSCs) in a murine critical limb ischemia (CLI) model. The isolated mitochondria were characterized to confirm their structural integrity, purity, and ATP production capacity before transplantation into an ischemic hindlimb. Results showed that mitochondrial transplantation significantly improved blood flow and muscle regeneration compared to MSC transplantation, as evidenced by laser Doppler perfusion imaging and histological analysis. Enhanced ATP production and increased oxidative phosphorylation complex protein levels were observed, supporting energy metabolism in ischemic conditions. Mitochondrial transplantation also reduced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS) levels and increased antioxidant enzyme expression, including SOD-2, leading to reduced oxidative stress and apoptosis, as indicated by decreased Bax, cytosolic cytochrome c, and cleaved caspase-3 levels. Furthermore, mitochondrial transplantation promoted angiogenesis and increased vascular density in ischemic muscles by enhancing endothelial cell function. Overall, PD-MSC-derived mitochondrial transplantation demonstrated proved more effective over MSC transplantation in reducing inflammation, restoring mitochondrial function, and supporting tissue recovery, highlighting its promise as an effective therapeutic approach for CLI and other ischemic conditions by directly addressing mitochondrial dysfunction and overcoming the limitations of conventional cell therapies.