2020년 03월 Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium improves insulin resistance in C2C12 cell
첨부파일
-
 2020-03 Umbilical cord-MSC-conditioned medium improves insulin resistance in C2C12 cell.pdf
(378.1K)
8회 다운로드
DATE : 2020-07-14 14:18:47
2020-03 Umbilical cord-MSC-conditioned medium improves insulin resistance in C2C12 cell.pdf
(378.1K)
8회 다운로드
DATE : 2020-07-14 14:18:47
관련링크
본문
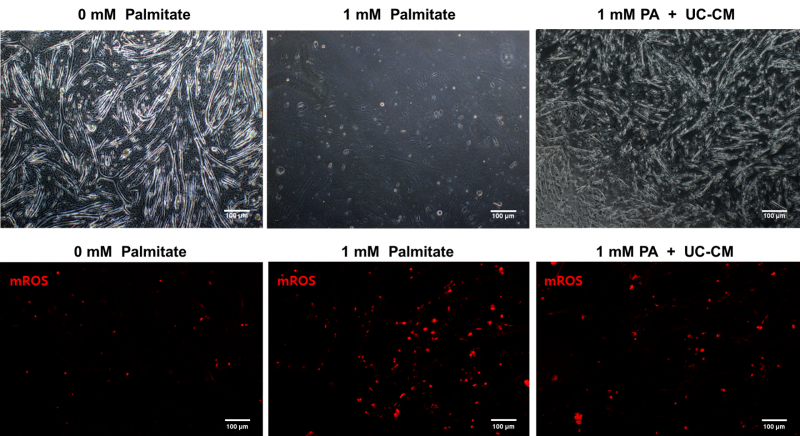
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium (UC-MSC-CM) has emerged as a promising cell-free therapy. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effects of UC-MSC-CM on insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cell. Insulin resistance was induced by palmitate. Effects of UC-MSC-CM on insulin resistance were evaluated using glucose uptake,
glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation, insulin signaling pathway, and mitochondrial contents and function in C2C12 myotubes. Glucose uptake was improved by UC-MSC-CM up to 60% (P < 0.05). UC-MSC-CM treatment increased only in membranous GLUT4 expression not in cytosolic GLUT4 expression. It restored insulin signaling pathway in insulin receptor substrate 1 (Ser307, Ser612) and AKT. Mitochondrial contents evaluated by mtTFA, PGC-1α were increased by UC-MSC-CM. In addition, UC-MSC-CM significantly decreased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (up to 50%, P < 0.05) and increased membrane potential (up to 15%, P < 0.05). However, there were no significant improvements in mitochondrial dynamics and ATP contents. Cytokine and active factor analysis of UC-MSC-CM showed that it contained many regulators inhibiting insulin
resistance such as TIMP-2, SPARC, MCP-1, VEGF, GDF-15, and angiopoietin-1. These results suggest that UC-MSC-CM improves insulin resistance with multiple mechanisms in skeletal muscle.
glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation, insulin signaling pathway, and mitochondrial contents and function in C2C12 myotubes. Glucose uptake was improved by UC-MSC-CM up to 60% (P < 0.05). UC-MSC-CM treatment increased only in membranous GLUT4 expression not in cytosolic GLUT4 expression. It restored insulin signaling pathway in insulin receptor substrate 1 (Ser307, Ser612) and AKT. Mitochondrial contents evaluated by mtTFA, PGC-1α were increased by UC-MSC-CM. In addition, UC-MSC-CM significantly decreased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (up to 50%, P < 0.05) and increased membrane potential (up to 15%, P < 0.05). However, there were no significant improvements in mitochondrial dynamics and ATP contents. Cytokine and active factor analysis of UC-MSC-CM showed that it contained many regulators inhibiting insulin
resistance such as TIMP-2, SPARC, MCP-1, VEGF, GDF-15, and angiopoietin-1. These results suggest that UC-MSC-CM improves insulin resistance with multiple mechanisms in skeletal muscle.